In an era defined by rapid digital transformation and escalating cyber threats, the strategic imperative of risk management in information technology security has never been more critical. Businesses globally navigate a complex landscape where technological advancements bring immense opportunities but also introduce sophisticated vulnerabilities. Understanding how to identify, assess, mitigate, and continuously monitor these risks is not merely a technical task; it is a fundamental pillar of modern business continuity and competitive advantage. Today, DoctinOnline will accompany you to explore the multifaceted domain of IT security risk management, providing deep insights into its core principles, practical applications, and the cutting-edge technologies shaping its future. This article aims to equip technology enthusiasts, IT professionals, and business leaders with the knowledge to fortify their digital defenses and make intelligent decisions in a constantly evolving threat environment.
Understanding the Core of IT Security Risk Management
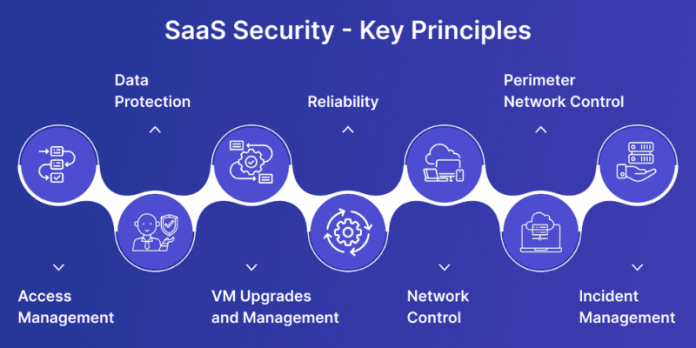
Risk management in information technology security is a systematic process designed to protect an organization’s information assets from an ever-growing array of cyber threats. It encompasses the policies, procedures, and technologies deployed to mitigate risks arising, “Effective cybersecurity is not a product, but a process.” This emphasizes the ongoing, dynamic nature of securing digital assets, demanding constant vigilance and adaptation to new threats and vulnerabilities.
The Evolving Threat Landscape And Its Economic Impact
The digital battleground is increasingly volatile, with cybercriminals and state-sponsored actors continually refining their tactics. The sheer scale and sophistication of modern cyber threats pose significant financial, reputational, and operational risks to organizations of all sizes. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, phishing campaigns, and supply chain compromises represent the most prominent dangers, each capable of inflicting substantial damage. Understanding these pervasive threats is the first step toward building resilient defenses.
The economic repercussions of cyber incidents are staggering and continue to rise. In 2024, the average global cost of a data breach reached a formidable $4.88 million, marking a 10% increase, with the United States experiencing an average cost of $9.36 million, averaging $9.77 million. Financially motivated actors frequently employ a Ransomware-as-a-Service model, making sophisticated attack tools accessible to a wider range of criminals. Trends for 2025 indicate a continued shift towards data exfiltration without encryption, where attackers threaten to publicly release sensitive data to extort payments. Critical manufacturing, financial services, information technology, and government sectors are consistently high-value targets. Furthermore, supply chain cyber attacks impacted 183,000 customers in 2024, representing a 33% increase, “Cybercrime is the greatest threat to every company in the world.”
Foundational Frameworks And Key Components

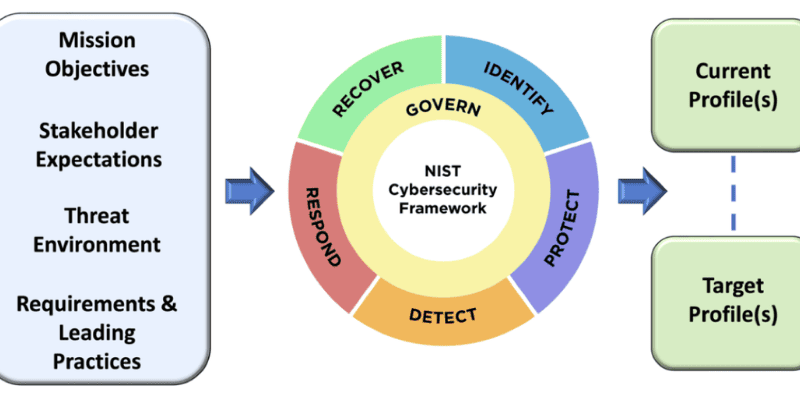
To effectively navigate the complex threat landscape, organizations rely on established frameworks that provide a structured approach to risk management in information technology security. These frameworks offer comprehensive guidance, ensuring that security efforts are consistent, repeatable, and aligned with industry best practices and regulatory requirements. Two prominent examples are the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) and ISO 27001.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Risk Management Framework provides a flexible, 7-step process that integrates security, privacy, and cyber supply chain risk management activities throughout the system development lifecycle. It offers a robust methodology for federal agencies and a widely adopted standard for private organizations, helping them manage information security and privacy risks effectively. Similarly, ISO 27001, an international standard for information security management systems (ISMS), offers a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and treating information security risks. Its core principle is to help companies make informed decisions about information security risks through a consistent and repeatable risk management strategy.
Key components of an effective cyber risk management framework include:
- Asset identification and valuation: Cataloging all critical IT assets,.
- Threat and vulnerability assessment: Identifying potential dangers that could exploit weaknesses in assets and evaluating existing security flaws within systems and applications. Regular vulnerability scans are crucial.
- Risk assessment and prioritization: Analyzing the likelihood and potential impact of identified threats exploiting vulnerabilities, then prioritizing risks based on their severity. Not all risks are created equal, and resources must be allocated strategically.
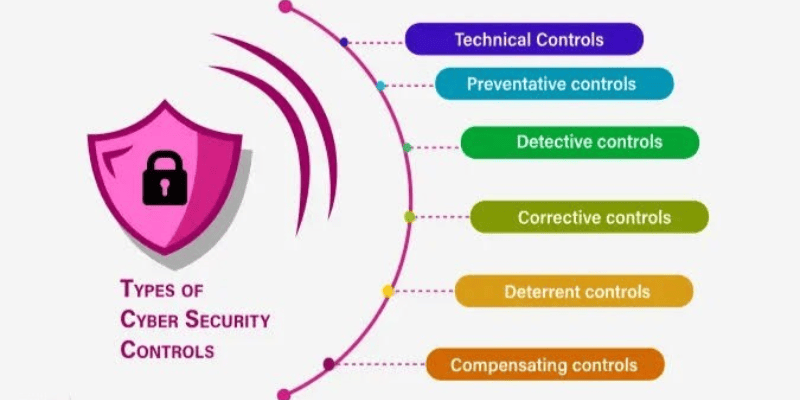
- Security controls implementation: Deploying appropriate technical and administrative safeguards, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, endpoint protection, and robust employee training, to mitigate identified risks.
- Incident response planning: Developing comprehensive plans outlining procedures for detection, containment, eradication, and recovery in the event of a security incident. Companies with established plans can reduce recovery costs by up to 50%.
- Continuous monitoring and review: Regularly assessing the effectiveness of implemented controls, monitoring for new threats and vulnerabilities, and updating the risk management framework to adapt to changing conditions.
- Compliance adherence: Ensuring that security practices align with industry regulations and data privacy laws, which is integral to demonstrating a commitment to information security and mitigating cyber risks.
Strategic Implementation For Robust Security Posture
Implementing an effective risk management in information technology security strategy requires a multifaceted approach that extends beyond mere technical controls. It involves fostering a security-conscious culture, leveraging human intelligence, and establishing resilient processes. Organizations must move toward a layered security model, recognizing that no single defense mechanism is foolproof. This strategy embraces the concept that if one security layer is breached, others are in place to detect and contain the threat.
Developing and refining risk mitigation strategies is paramount. The ISO 27001 standard outlines four broad ways to respond to identified risks: modifying the risk through security measures, sharing the risk with another party (e.g., through insurance or outsourcing), avoiding the threat altogether, or actively retaining the risk after a conscious decision. The choice depends on the organization’s risk appetite and the feasibility of each option. For instance, a major healthcare provider successfully implemented robust access controls, which resulted in a 25% decrease in unauthorized access attempts, demonstrating the tangible benefits of a focused mitigation strategy.
The human element plays a significant role in cybersecurity, often being both the strongest asset and the weakest link. Statistics show that the human element is the common root cause of 68% of data breaches. Therefore, investing in comprehensive employee training and security awareness programs is crucial. These programs should educate staff on phishing scams, social engineering tactics, strong password practices, and the importance of reporting suspicious activities. As the cybersecurity quote emphasizes, “Your employees are your biggest risk—and your greatest defense.” Transforming employees into a proactive line of defense dramatically strengthens an organization’s overall security posture.
Managing third-party and supply chain risks has also become increasingly vital. As organizations rely on a web of vendors and partners, the security posture of these external entities directly impacts their own. Gartner predicts that 60% of supply chain organizations will use cybersecurity risks as critical evaluation criteria for third-party business engagements and transactions. Implementing rigorous vendor selection processes, conducting regular security audits of third-party providers, and establishing clear contractual obligations for security are essential steps. A financial institution, for example, tightened its vendor selection criteria, leading to a notable 35% decline in third-party risk exposures, showcasing the direct impact of robust supply chain risk management.
Leveraging Advanced Technologies For Proactive Defense
The rapid evolution of advanced technologies, particularly Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), is fundamentally transforming the landscape of risk management in information technology security. These technologies offer unprecedented capabilities for predictive analytics, real-time threat detection, and automated responses, enabling organizations to move. AI-powered tools can analyze vast datasets to identify subtle patterns and anomalies that indicate potential threats, often far more quickly and accurately than human analysts.
One of the most significant advancements is the integration of AI into Zero Trust architecture. The Zero Trust model, built on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” assumes that no user, device, or application, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. AI enhances this framework by providing continuous, real-time verification and access control based on dynamic risk assessments. For instance, AI-driven analytics can continuously evaluate user behavior, device security posture, and network conditions to make context-aware access decisions, dynamically adjusting access levels in response to evolving threats. This capability allows for more granular control and significantly reduces the attack surface.
Cloud computing, while offering immense flexibility and scalability, introduces its own set of security challenges. Misconfigurations and inadequate API security are common vulnerabilities that attackers exploit, allowing them to move laterally between systems. Advanced risk management strategies in cloud environments leverage AI to monitor cloud activity, identify misconfigurations, and enforce security policies automatically. The concept of a shared responsibility model, where both the cloud provider and the client have defined security duties, is paramount for securing applications and assets effectively within this distributed infrastructure.
Automation, driven by AI and ML, is also revolutionizing security operations. AI can accelerate the implementation of Zero Trust principles by automating routine security tasks, such as data classification, threat detection, and initial incident response. This frees up valuable security team resources to focus on complex investigations, strategic planning, and addressing critical issues. Predictive AI reinforces Zero Trust principles, enhances real-time threat detection, and improves data security, backup, and recovery processes. A notable case study from RAZE Banking highlights the power of AI: by implementing an AI solution with predictive analytics, the bank achieved a 45% reduction in fraudulent transactions and a 30% improvement in operational efficiency, demonstrating the tangible benefits of AI in combating financial and cyber risks.
Conclusion
The digital future promises both unprecedented innovation and increasingly sophisticated threats. For businesses to thrive in this environment, a robust and adaptive approach to risk management in information technology security is no longer optional—it is a strategic imperative. By understanding the evolving threat landscape, adopting comprehensive frameworks, and embracing advanced technologies like AI and Zero Trust, organizations can build resilient defenses that protect their critical assets, ensure operational continuity, and maintain customer trust. The journey toward optimal security is continuous, demanding constant vigilance, proactive strategies, and a culture of shared responsibility. DoctinOnline remains committed to providing you with the most authoritative and up-to-date insights to navigate these complexities, empowering you to make intelligent investment and adoption decisions that secure your digital future. Continue to explore our resources to stay ahead in the dynamic world of technology and cybersecurity.